Entire Set of Printable Figures For
Categorization and Acquired Equivalence - Urcuioli
Figure 1.
Non-human














Human














![]()
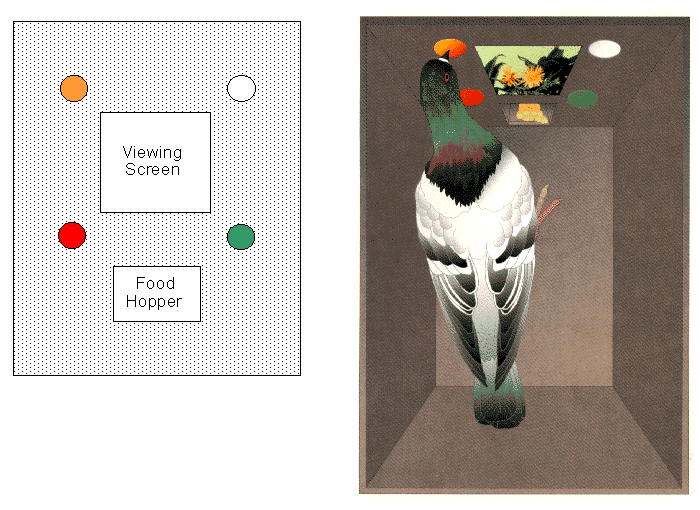
Figure 2. The display and response apparatus used in the categorization-by-appearance studies by Bhatt et al. (1998).
![]()
Figure 3.
Humans








Flowers








Cars








Chairs








![]()
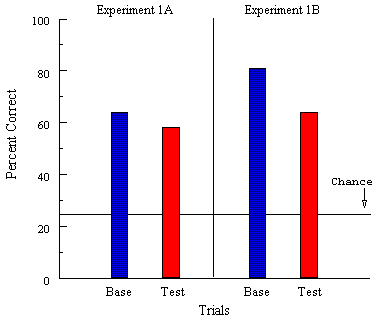
Figure 4. Percentage of trials in which pigeons correctly classified pictures of cats, chairs, cars and flowers in Bhatt et al. (1988). Base = baseline (training) trials with familiar pictures, Test = trials with novel pictures.
![]()
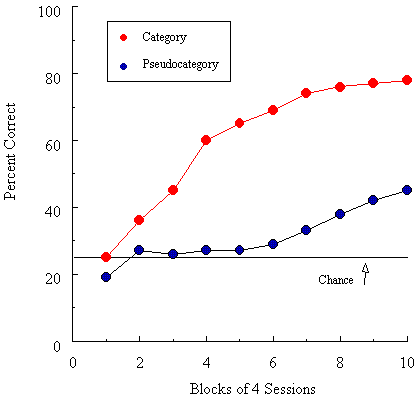
Figure 5. Acquisition of category vs. pseudocategory discriminations by pigeons. (Adapted from Wasserman et al., 1988).
![]()
Animation can't be printed
![]()
Figure 6. A design to assess categorization by common reward associations.

![]()
Figure 7. Transfer of matching across samples with common reward associations. Base = baseline accuracy with familiar samples, Test = accuracy of choice with novel samples.
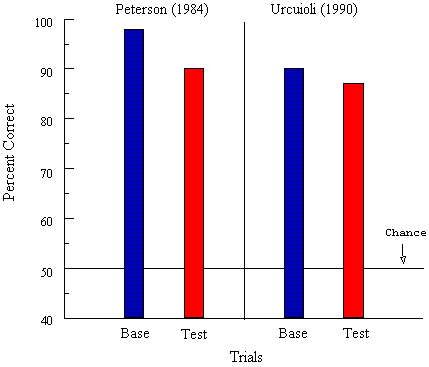
![]()
Figure 8.
![]()
Demo can't be printed
![]()
Figure 9. Categorization-by-association results from Wasserman et al. (1992). Baseline = choice accuracy with explicitly trained samples, Test = choice accuracy with "untrained" samples.
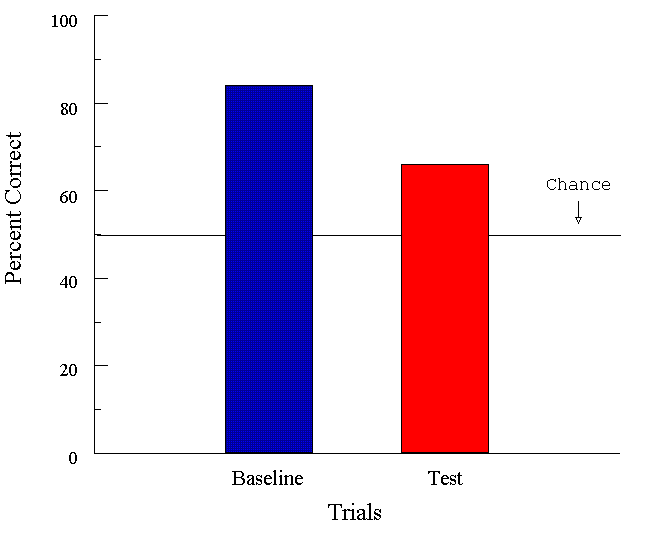
![]()
Figure 10. Categorization-by-association results for six pigeons from Urcuioli et al. (1989, Experiment 2) over the initial trials of transfer testing.
![]()
Video can't be printed
![]()
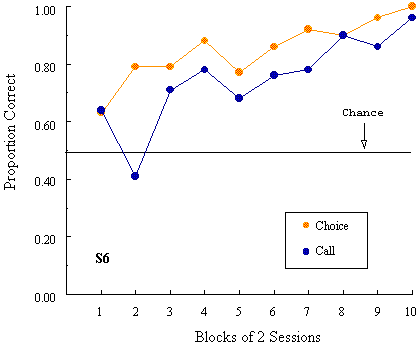
Figure 11. Proportion of correct choices following, and proportion of categorization-consistent calls to, the newly introduced samples in the many-to-one task of Manabe et al. (1995, Experiment 3).
![]()
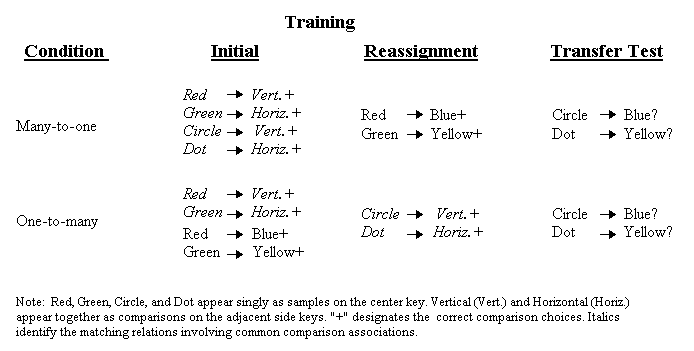
Figure 12. A design to compare transfer following Many-to-one vs. One-to-many training.
![]()
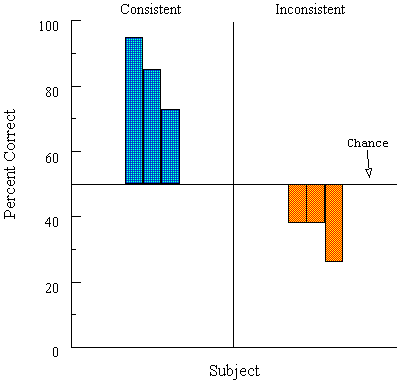
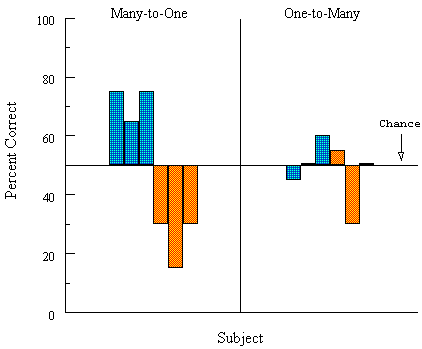
Figure 13. Categorization-by-association results after many-to-one and a control (one-to-many) training condition for consistently and inconsistently tested pigeons (blue and orange bars, respectively) in Urcuioli et al. (1995, Experiment 2).
![]()
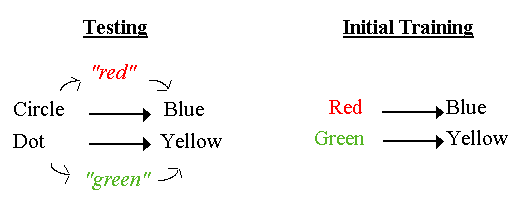
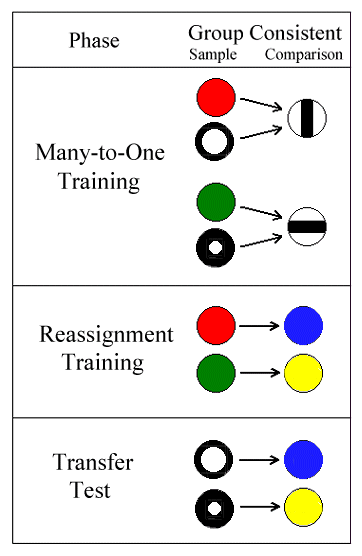
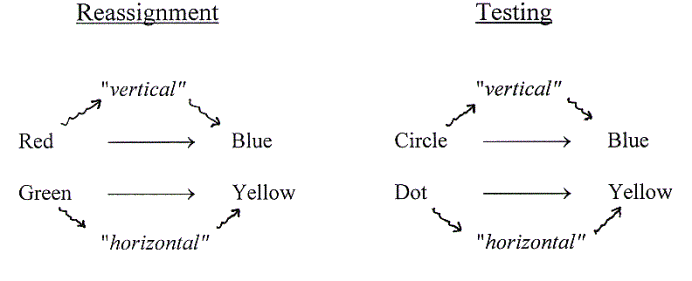
Figure 14. Note: Red, Green, Circle, and Dot are samples. Blue and Yellow are correct choice alternatives.
![]()
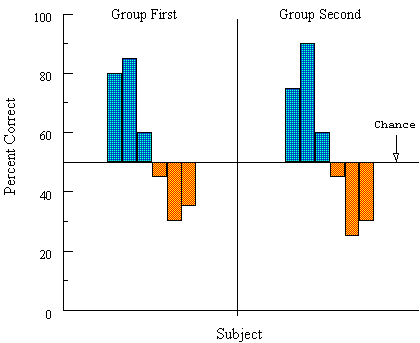
Figure 15. Categorization-by-association results for consistently and inconsistently tested pigeons (blue and orange bars, respectively) when many-to-one training preceded (Group First) or followed (Group Second) learning of different choices to two of the many-to-one samples.
![]()
Animation can't be printed
![]()
Animation can't be printed
![]()
Figure 16. A retrospective mediational account of transfer.