Training Procedure.
The initial phase of most of the experiments (except
where noted otherwise) involved training with a four-key choice procedure.
Each pigeon was trained to discriminate among line drawings of four different
objects, such as a watering can, an iron, a desk lamp, and a sailboat.
The training objects were displayed individually in the center of a video
monitor on different trials. 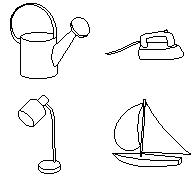 The pigeon had to initially peck at the object
on the viewing screen in order to obtain access to four differently-colored
choice keys. The choice keys were situated diagonally from each corner
of the viewing screen. Each object was associated with a different choice
key. For example, one pigeon might have to peck the red key in the presence
of the watering can, the green key in the presence of the iron, the blue
key in the presence of the desk lamp, and the violet key in the presence
of the sailboat. Different birds recieved different object-choice key assignments.
If the pigeon pecked the correct choice key, then food reinforcement was
delivered to a food tray located on the back wall of the chamber. If the
pigeon chose the incorrect key, then the trial was repeated until a correct
choice was made, resulting in the delivery of food. Training sessions were
conducted daily until the birds attained a high level of accuracy (e.g.,
75% correct to each object).
The pigeon had to initially peck at the object
on the viewing screen in order to obtain access to four differently-colored
choice keys. The choice keys were situated diagonally from each corner
of the viewing screen. Each object was associated with a different choice
key. For example, one pigeon might have to peck the red key in the presence
of the watering can, the green key in the presence of the iron, the blue
key in the presence of the desk lamp, and the violet key in the presence
of the sailboat. Different birds recieved different object-choice key assignments.
If the pigeon pecked the correct choice key, then food reinforcement was
delivered to a food tray located on the back wall of the chamber. If the
pigeon chose the incorrect key, then the trial was repeated until a correct
choice was made, resulting in the delivery of food. Training sessions were
conducted daily until the birds attained a high level of accuracy (e.g.,
75% correct to each object).
Testing Procedure. Testing with different kinds of stimulus manipulations occurred following
training on the original task. Test stimuli were presented in sessions
along with normal training trials and their occurrence was relatively rare
(e.g., 16% of the trials). On training trials, the normal contingencies
were in place (correction trials for an incorrect response and food reward
for a correct response). On test trials, food reinforcement was delivered,
regardless of the pigeon's initial choice response. If performance
on the training trials fell below a criterion (e.g., 75% correct on each
key), then one or more retraining sessions were administered to re-establish
accurate performance on the original discrimination.
![]()